In this article:
Project #2 – Green Energy for the Processing Facility
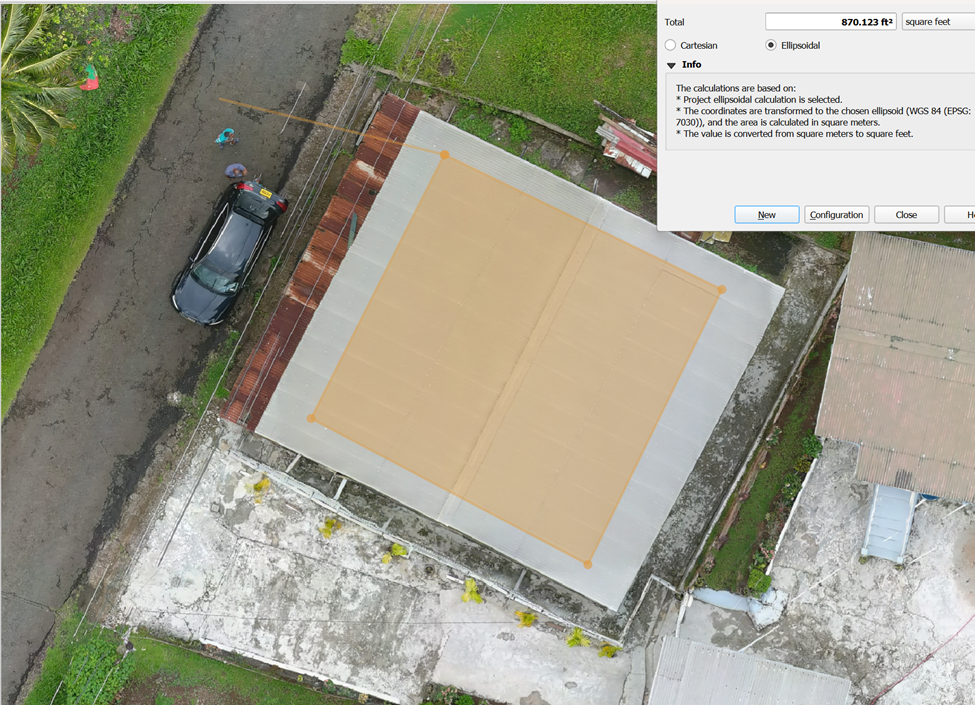
Here are the design considerations for your 10 kW three-phase solar system on a roof with 822 sq. ft. of usable space and 8 hours of sunshine per day:
1. System Capacity and Panels
- Power Requirement: 10 kW (10,000 watts) system.
- Total space required=25 panels×20 sq. ft. per panel=500 sq. ft.
This comfortably fits within your available 822 sq. ft.
2. Orientation and Tilt
- Optimal Orientation: Panels should face north (if in the southern hemisphere) for maximum exposure.
- Tilt Angle: The optimal tilt angle is typically equal to your location’s latitude to maximize yearly sunlight capture. For cleaning purposes, a tilt angle of 10-15° helps prevent debris buildup. The design has bee proposed to ensure that orientation for maximum sunlight exposure is gained.

3. Shading Analysis
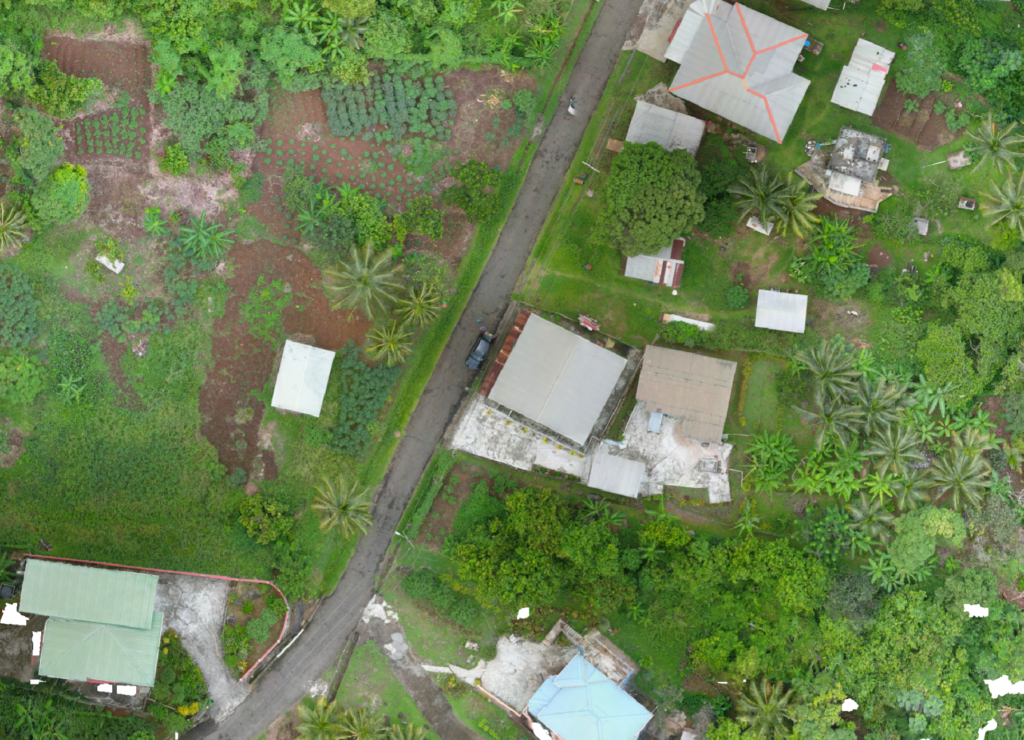
- Ensure no shading from surrounding buildings, trees, or parapet walls that could reduce panel efficiency during peak sun hours. The above image show the current layout and exposure to sunlight.

4. Inverter Selection
- Inverter Type: A three-phase inverter is necessary for your system. Choose an inverter rated for 15 kW output, compatible with grid-tied or off-grid requirements based on your preferences.
- Microinverters or Power Optimizers: Consider these to reduce shading impact and improve overall efficiency.
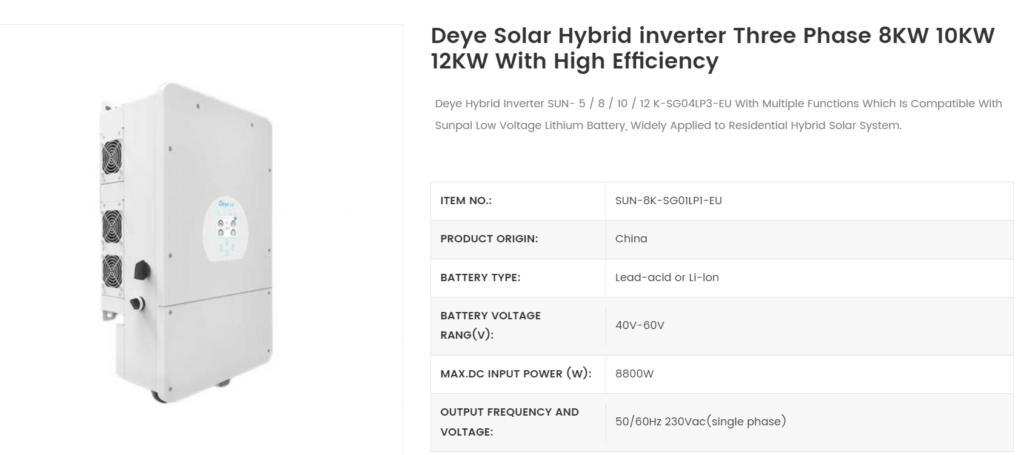
- Choice of Inverter is Hybrid 3 Phase type inverter _ DEYE inverter
- (https://www.sunpalsys.com/deye-solar-hybrid-inverter-three-phase-8kw-10kw-12kw-with-high-efficiency_p300.html)
- Deye Hybrid Inverter is applied to our hybrid systems seamlessly adjust to fluctuations in power from both the utility and the solar array maximizing the energy storage and consumption.With a number of different configuration settings users can decide when and how much energy is stored or sold back to the utility.Integration has never been easier or more simplified,our Deye inverter allows seamless integration with solar array and battery bank.
5. Electrical Components
- Cabling: Use weather-resistant cabling for outdoor applications. For a three-phase system, make sure cables can handle the load and ensure efficient distribution.
- Surge Protection: Install surge protectors to safeguard the system from lightning or power surges.
- Three-phase Distribution Box: For balanced load sharing among the three phases.
6. Battery Storage:
- Battery Bank: If you plan to include storage, size the battery bank to store sufficient energy for evening use or backup, considering the capacity and autonomy desired.
- Based on the nightly consumption the battery bank to store of 2.5Kw per house (kw/h) we are seeking to ensure that the storage facility can operate the cooling systems during the night and thus battery system such s 40kw/h storage system is recommended. 48V 400Ah.
7. Roof Structure
- Weight Considerations: Ensure the roof can support the weight of the panels and mounting hardware. High-efficiency panels weigh around 40-50 lbs per panel.
- Wind Loading: Ensure the mounting system is robust enough for your region’s wind conditions (e.g., hurricane-resistant design).
8. Walkway and Maintenance
- Keep clear paths for easy access to the panels for cleaning, inspection, and maintenance. The available space of 822 sq. ft. allows sufficient space for maintenance walkways around the system.
9. Regulatory and Safety Compliance
- Local Regulations: Ensure compliance with local building codes, fire safety standards, and grid-connection requirements.
- Fire Safety: Ensure access to a rapid shutdown system for emergency services as per NEC 2017 standards (or your local equivalent).
Would you like further breakdowns, such as specific component recommendations or a cost estimate?
Design items for consideration
When designing a three-phase hybrid solar system for a 400V configuration with battery storage (targeting between 10 kW to 15 kW of solar generation), there are more powerful and efficient options than a 48V 200Ah battery. Higher voltage battery systems offer advantages in terms of efficiency, lower current, and reduced wiring requirements. Let’s consider both the 400V system and alternatives to the 48V 200Ah batteries.
1. Battery Type for a 400V System
For a 400V system, higher voltage battery banks are typically more suitable, as they allow the system to operate more efficiently with lower current, reducing losses in transmission. Here are some options:
Higher Voltage Batteries (Better Than 48V 200Ah)
- Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4) 96V or 400V Systems:
- Why Higher Voltage Batteries?:
- Higher voltage systems (e.g., 96V or 400V) reduce the current in the system, leading to reduced wire size and lower transmission losses.
- They are more efficient and can handle larger commercial loads more effectively.
- Lithium-Ion systems are still the best choice for commercial-grade energy storage due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and minimal maintenance.
- Examples of High-Voltage Battery Systems:
- Tesla Powerwall 2:
- Nominal voltage: 350V to 450V
- Energy capacity: 13.5 kWh per unit
- Multiple units can be stacked to increase storage to 40 kWh or more.
- LG Chem RESU HV:
- Nominal voltage: 400V
- Energy capacity: 9.8 kWh per unit (can be stacked).
- Pylontech Force H2:
- Nominal voltage: 384V to 512V
- Scalable: Can stack multiple units for higher capacity.
- Designed for hybrid and commercial applications.
- BYD B-Box HV:
- Nominal voltage: 200V to 500V
- Energy capacity: 11.5 kWh per module.
- Modular and scalable design.
- Why Higher Voltage (400V) Batteries are Better for 400V Three-Phase Systems:
- Lower current: Higher voltage reduces the current in the system, which means less heat, less power loss, and the ability to use thinner cables.
- Increased efficiency: Less energy is lost in the process, making the system more efficient.
- Scalability: These systems are modular, so you can expand the battery bank as energy demand increases.
2. Hybrid Inverter for a 400V System
For a three-phase hybrid system (10 kW to 15 kW) operating at 400V, the inverter must handle both the solar PV array and battery storage efficiently. Recommended options:
Recommended Hybrid Inverter:
- SMA Sunny Tripower Core 1:
- Power rating: 15 kW three-phase
- Input voltage range: 150V to 1,000V (perfect for 400V battery systems).
- Battery integration: Can work with high-voltage battery banks, such as the Tesla Powerwall or BYD B-Box HV.
- Efficiency: 98.1% efficiency, with grid-tied and off-grid functionality.
- Fronius Symo Hybrid:
- Power rating: 10 kW or 15 kW three-phase.
- Input voltage: Compatible with 400V systems.
- Battery integration: Supports high-voltage battery banks.
- Smart monitoring: Advanced monitoring features with Wi-Fi/Ethernet options.
- Huawei SUN2000 Series:
- Power rating: 10 kW to 15 kW.
- Input voltage range: 200V to 800V.
- Battery integration: Optimized for high-voltage battery systems, including 400V configurations.
These inverters are designed to handle high-voltage batteries and three-phase systems, ensuring compatibility with a 400V system.
3. Solar Panels for the System
For a 10 kW to 15 kW system, you should select high-efficiency solar panels to maximize energy generation:
Recommended Solar Panels:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels:
- Power Rating: Use panels rated at 500W to 550W to optimize space and efficiency.
- Number of Panels:
- For a 10 kW system: 18 to 20 panels of 500W to 550W.
- For a 15 kW system: 28 to 30 panels of 500W to 550W.
- Brands: SunPower, LG, Canadian Solar, Trina Solar, LONGi.
Panel Configuration:
- Ensure the panels are wired in series to achieve the desired voltage for input into the inverter (typically 800V DC for a 400V three-phase inverter).
4. Cabling for a 400V Three-Phase System
DC Cabling (from solar panels to inverter):
- Cable Type: PV-rated cables, typically single-core, double-insulated DC cables.
- Cable Size: With a higher voltage (e.g., 800V DC from the solar panels), the current will be lower, so you can use 6mm² to 10mm² cables for the DC side.
AC Cabling (from inverter to distribution):
- For the AC side, you’ll need three-phase AC cabling rated for the 400V output. Ensure you use fire-rated cables with appropriate insulation for commercial use.
- Cable Size: AC cables should be 4mm² to 10mm², depending on the distance and load.
Battery Cabling:
- Use higher gauge cables (e.g., 25mm² to 50mm²) to minimize voltage drop and ensure efficient power transfer between the battery and inverter.
5. Other Essential Solar Devices
- Combiner Box:
- Purpose: Combines multiple strings of PV modules before they are fed into the inverter.
- Rating: Ensure it is rated for the voltage (800V DC) and current of your solar array.
- Surge Protection Devices (SPDs):
- Type 1 and Type 2 SPDs: Protect the system from surges and lightning strikes. Install SPDs on both the AC and DC sides.
- Disconnect Switches:
- Install DC and AC disconnects to safely isolate the solar array and batteries for maintenance.
- Battery Management System (BMS):
- A BMS is critical for high-voltage battery systems like LiFePO4. It ensures the batteries charge and discharge safely, preventing issues like overcharging or deep discharge.
- Racking System:
- Tilted Roof or Ground-Mounted Racking: For commercial installations, choose a durable aluminum or galvanized steel racking system. It should withstand local weather conditions (e.g., wind loads, storms).
Summary
For a 400V three-phase hybrid solar system (10 kW to 15 kW), the best options include:
- Higher voltage batteries like Tesla Powerwall 2, LG Chem RESU HV, or BYD B-Box HV that operate at 400V and provide scalable energy storage with high efficiency.
- Hybrid inverters such as SMA Sunny Tripower Core 1 or Fronius Symo Hybrid, capable of handling high-voltage battery banks and three-phase loads.
- Monocrystalline solar panels in the 500W to 550W range for maximum efficiency.
- Appropriately sized DC and AC cabling with surge protection, disconnects, and BMS for safety and reliability.
This design offers scalability, high efficiency, and low losses, making it ideal for commercial solar systems. Would you like more details on any specific component?
